Picture this: it’s the late 1950s, and nations are competing to conquer the last uncharted frontier – space! The Space Race is on, and the United States and the Soviet Union are neck and neck in pursuing the stars. This exciting period witnessed the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, launched into orbit and the first human, Yuri Gagarin, bravely venturing into space. But what drove these pioneers to leave the safety of Earth and explore the vast cosmos?
The early days of space exploration were fueled by curiosity, scientific discovery, and a desire to show off technological prowess. Astronauts embarked on daring missions to learn more about the universe, conduct groundbreaking research, and see how far humans could go. From Alan Shepard’s suborbital flight to Neil Armstrong’s legendary moonwalk, these intrepid explorers pushed the boundaries of human knowledge and paved the way for future generations of astronauts.
The Role of the Cold War
After World War 2, the United States and the Soviet Union became rivals, each trying to one-up the other on the cosmic playground. This high-stakes game of “anything you can do, I can do better” became known as the Space Race.
So, what was the Cold War all about? It was a period of intense rivalry and tension between the Western Bloc, led by the United States, and the Eastern Bloc, led by the Soviet Union. Both sides wanted to prove their superiority in terms of political, economic, and technological prowess. And what better way to flex their muscles than by showing off their ability to conquer space?

As the Space Race kicked off, the world watched in awe as both nations raced to achieve incredible milestones. The Soviets took the lead, launching Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite, and sending cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, the first human, into space. The United States, not to be outdone, pushed forward with its space program, eventually putting a man on the Moon – an unforgettable moment as Neil Armstrong took his “one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.”
Throughout this epic showdown, the role of astronauts became increasingly important. These brave men and women were at the forefront of humanity’s journey into the unknown, carrying out complex missions and making history with each new achievement. As a result, the Cold War fueled the fire of competition and played a significant part in driving advancements in space technology and exploration.
Scientific Research in Space
When astronauts venture into the cosmos, they’re not just going for a joyride; they’re on a mission to uncover new knowledge and answer some of our biggest questions about Earth and the universe.
You might wonder, “Why do astronauts go to space to study Earth?” Well, it’s a bit like trying to understand a painting – sometimes, you must step back and look at the whole picture to truly appreciate it. That’s where space comes in! By observing Earth from above, scientists can gain a unique perspective on our planet, allowing them to study everything from weather patterns to the effects of climate change.
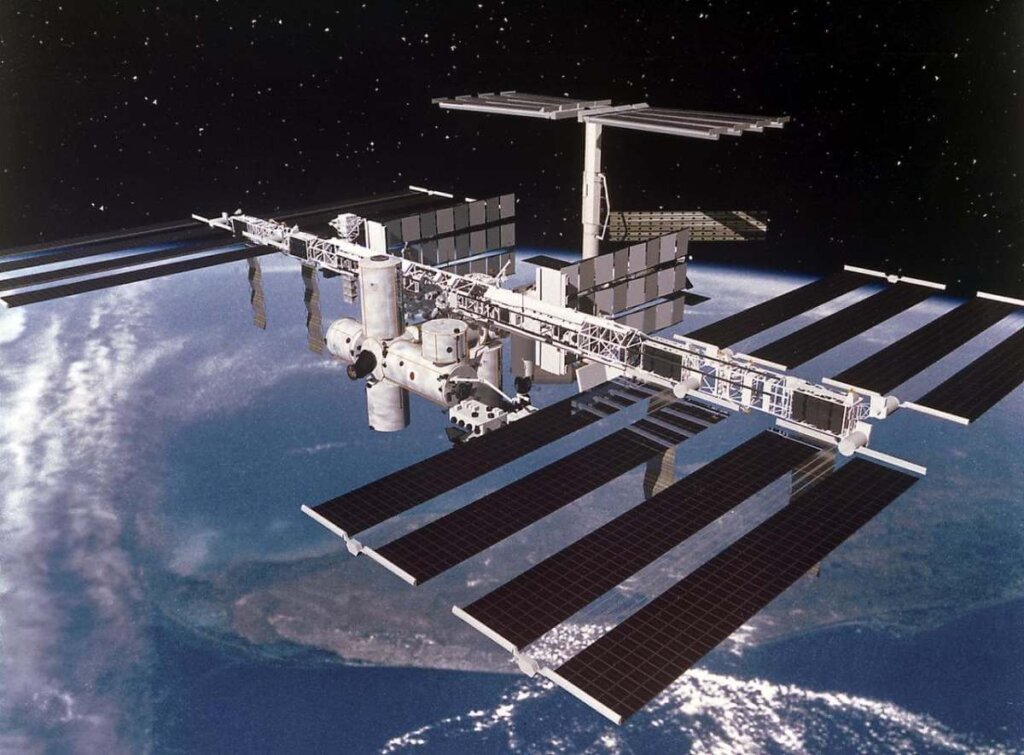

Astronauts play a crucial role in this research by conducting experiments, gathering data, and maintaining sophisticated instruments aboard spacecraft and space stations. This valuable information helps scientists back on Earth better understand our planet’s delicate ecosystems, track natural disasters, and monitor the impacts of human activities on the environment.
For example, satellites orbiting Earth constantly collect data on atmospheric conditions, which can be used to predict hurricanes and other severe weather events. This information helps meteorologists provide accurate forecasts and allows us to take precautions and protect lives and property.
The Study of Microgravity
The microgravity environment of space is another focus of research. Astronauts conduct experiments to investigate the effects of microgravity on physical and biological systems, which can help us understand how living organisms and materials behave in space and inform future space missions.
The Impact on Human Health
Astronauts also study the impact of space travel on human health. Long-duration space missions expose astronauts to unique health risks, such as radiation exposure and the effects of microgravity on the human body. Therefore, research in this area is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of future space travelers.
Astronomy and Astrophysics
Space exploration provides unparalleled opportunities for astronomers and astrophysicists to study celestial bodies, cosmic phenomena, and the universe’s origins. Observatories in space, like the Hubble Space Telescope, have revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos and fueled countless scientific discoveries.
Technological Advancements
Did you know space exploration has been a driving force behind many technological advancements we enjoy today? That’s right – the work of astronauts up in the cosmos has significantly impacted our lives down here on Earth. From satellite communication to life-saving medical devices, the innovations born from space exploration are nothing short of extraordinary.
When astronauts venture into space, they face an environment vastly different from our cozy little planet. Extreme temperatures, radiation, and the vacuum of space present a unique set of challenges that require innovative solutions. And this is where the magic happens!
Scientists and engineers are constantly developing new technologies and materials to overcome these challenges. Astronauts then test these innovations in the harsh space environment, providing valuable insights and feedback that help refine and perfect their design.
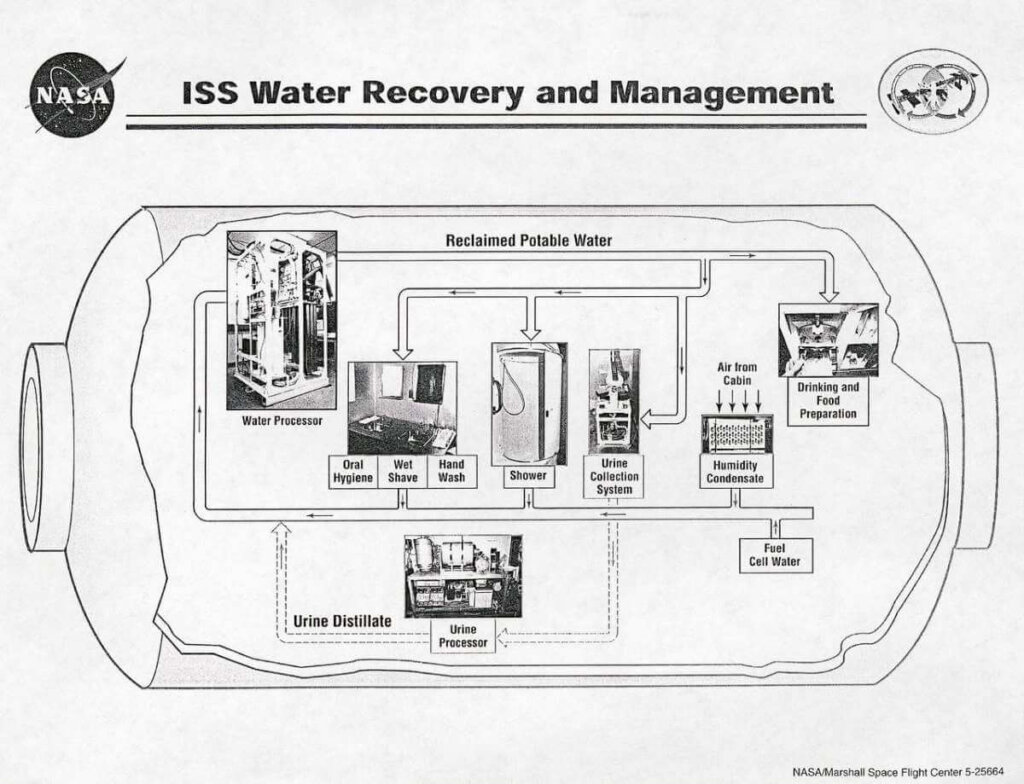
But these advancements don’t just stay in orbit. Many of the technologies initially developed for space exploration have been adapted for use on Earth, improving our daily lives in countless ways. For example, the development of water purification systems designed for use on the International Space Station. These systems have since been adapted for use in remote and disaster-stricken areas, providing clean drinking water to those in need.
Satellite Deployment and Maintenance
Another reason astronauts go to space is to deploy and maintain satellites. Satellites are crucial in modern society, providing essential services such as communication, weather forecasting, and GPS navigation. Astronauts are sometimes needed to perform repairs or upgrades on these valuable assets, ensuring their continued functionality.
International Collaboration and Diplomacy
The International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a prime example of how space exploration fosters international collaboration and diplomacy. Launched in 1998, the ISS is a joint project involving multiple countries, including the United States, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the European Space Agency. As a result, astronauts from different nations work together on the ISS, conducting research and sharing their findings with the global scientific community.
Collaborative Missions and Research
Beyond the ISS, many space missions and research projects result from international collaboration. These partnerships facilitate the sharing of resources, knowledge, and expertise, promote peaceful cooperation among nations, and help build trust and understanding.
The Impact on Education and Careers
Space exploration and astronauts’ accomplishments have inspired countless people to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Likewise, space travel excitement can motivate young people to learn about these subjects and consider pursuing careers in space-related fields.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, astronauts go to space for various reasons, including conducting scientific research, testing new technologies, fostering international collaboration, and inspiring future generations. The benefits of space exploration are vast, ranging from a deeper understanding of our universe to the development of new technologies that improve life on Earth. As we continue to explore the cosmos, the work of astronauts will remain crucial to our ongoing quest for knowledge and discovery.

