Moon phases have captivated humans for centuries, evoking a sense of wonder and intrigue. As we gaze up at the night sky, we witness the ever-changing appearance of the Moon, from a full, luminous orb to a mere sliver of light. But what exactly are moon phases, and how do they occur? Moon phases refer to the different shapes or appearances of the Moon as seen from Earth. These changes in the Moon’s appearance are a result of its position in relation to the Sun and Earth. The Moon does not emit its own light but instead reflects the sunlight that falls upon it.
Depending on its position in orbit around the Earth, different portions of the Moon are illuminated by the Sun, leading to the various phases we observe. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics behind moon phases, explore the different phases and their names, examine their durations, and discover how moon phases have influenced various cultural beliefs. So, let’s embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of moon phases and deepen our understanding of this celestial phenomenon.
What are Moon Phases and How Do They Occur?
To understand this captivating celestial dance, we must explore the dynamic relationship between the Moon, Earth, and the Sun. As the Moon orbits around our planet, different portions of its surface are illuminated by the Sun’s rays, giving rise to the distinct phases we observe. From the full brilliance of the full moon to the mysterious darkness of the new moon, each phase carries its own beauty and symbolism. It is important to note that moon phases are different from lunar eclipses as pictured below.
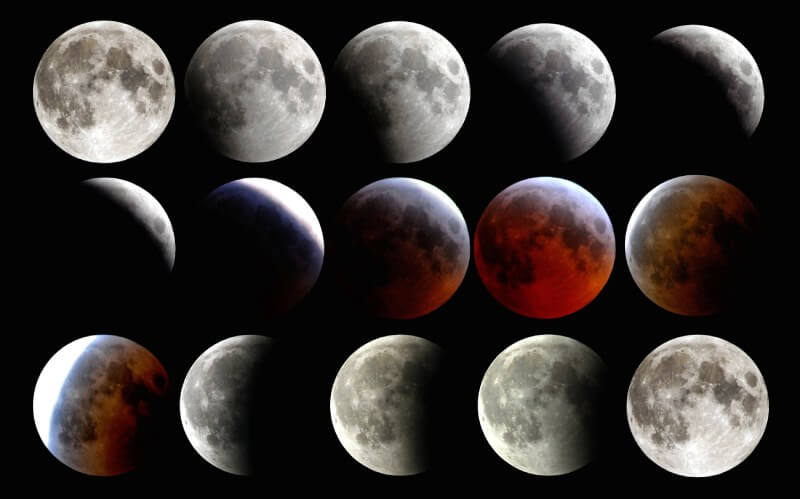

Why Does the Moon Appear to Change Shape?
The changing shape of the Moon, known as its phases, has intrigued and captivated humanity for centuries. Despite its unchanging spherical nature, our perspective from Earth creates the illusion of a shifting lunar landscape. But why does the Moon appear to change shape? The answer lies in the interaction between the Moon, Earth, and the Sun.
As the Moon orbits our planet, different amounts of sunlight are reflected back to us, creating the various phases we observe. From the dazzling brightness of the full moon to the slender crescent of the new moon, these apparent shape transformations are a result of the Moon’s position relative to the Earth and the Sun.
What Causes the Different Moon Phases?
The different phases of the Moon are caused by the relative positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun. As the Moon orbits around the Earth, different portions of its illuminated side become visible from our vantage point on Earth. This is because the Moon does not emit light of its own but reflects sunlight.
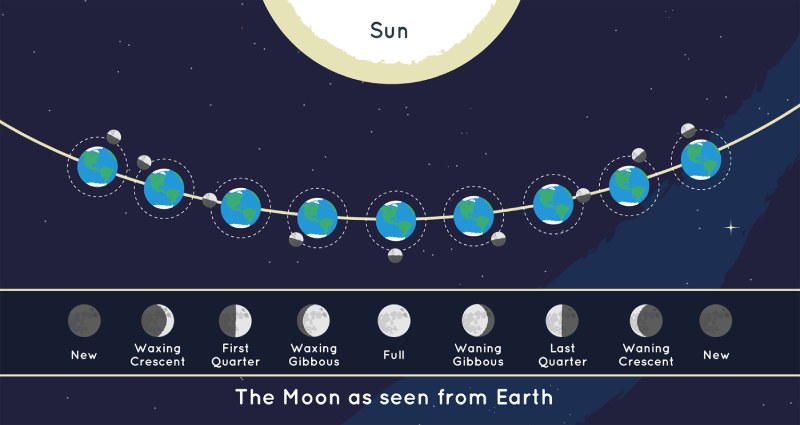
The changing angles and positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun determine the amount of sunlight that reaches different parts of the Moon’s surface, giving rise to the diverse phases we observe. This cyclic pattern of moon phases repeats approximately every 29.5 days, known as a lunar month, creating a rhythmic dance in the night sky that has fascinated and inspired humans throughout history.
How Many Primary Moon Phases Are There?
The Moon goes through eight distinct phases, starting with the new moon when it is positioned between the Earth and the Sun, making the side facing us appear dark. As the Moon continues its orbit, it gradually becomes more visible, transitioning through a waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, and eventually reaching the full moon when the entire illuminated side is facing us. After that, the Moon enters the waning gibbous, third quarter, and waning crescent phases before returning to the new moon.
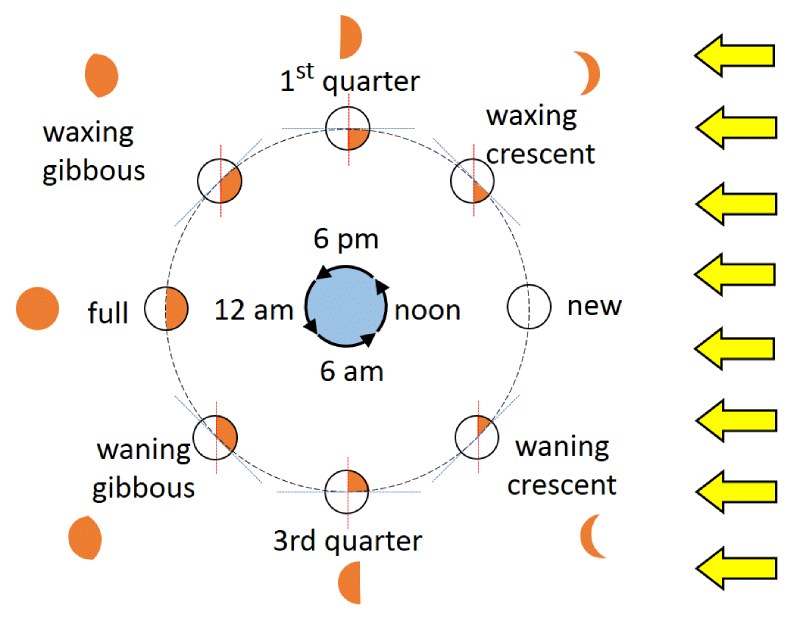
What are the Names of the Moon Phases?
The different phases of the Moon are commonly known by specific names that have been used for centuries. These names reflect the appearance of the Moon as it progresses through its monthly cycle. The names of the moon phases vary across different cultures and traditions, but there are commonly recognized terms used in many societies.
| Moon Phase | Description |
| New Moon | The Moon is not visible from Earth. |
| Waxing Crescent | A small sliver of the Moon is visible. |
| First Quarter | Exactly half of the Moon’s visible side is seen. |
| Waxing Gibbous | More than half of the Moon is visible and growing. |
| Full Moon | The entire illuminated side of the Moon is seen. |
| Waning Gibbous | More than half of the Moon is visible and shrinking. |
| Third Quarter | Exactly half of the Moon’s visible side is seen. |
| Waning Crescent | A small sliver of the Moon is visible. |
These names and descriptions capture the ever-changing appearance of the Moon as it transitions through its phases, offering a fascinating glimpse into the celestial rhythm that unfolds in the night sky.
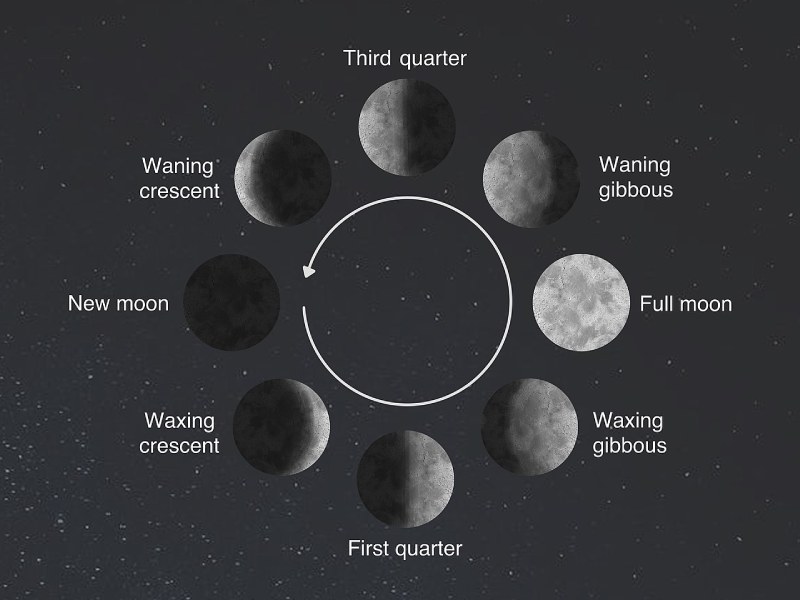
How Long Does Each Moon Phase Last?
The duration of each moon phase varies depending on the specific phase and its position in the lunar cycle. On average, a complete lunar cycle, from one New Moon to the next, takes approximately 29.5 days. However, the length of individual moon phases can differ.
Here is an estimate of the duration for each primary moon phase:
- New Moon: The New Moon phase lasts for about 1 to 3 days.
- Waxing Crescent: This phase lasts around 3 to 6 days.
- First Quarter: The First Quarter phase lasts about 6 to 7 days.
- Waxing Gibbous: This phase typically lasts around 7 to 10 days.
- Full Moon: The Full Moon phase lasts for about 1 to 3 days.
- Waning Gibbous: This phase lasts around 7 to 10 days.
- Third Quarter: The Third Quarter phase lasts about 6 to 7 days.
- Waning Crescent: This phase typically lasts around 3 to 6 days.
It’s important to note that these durations are approximate and can vary slightly from one lunar cycle to another. The actual length of each phase depends on various factors, including the position of the Moon in its orbit around the Earth and the angle of sunlight illuminating the Moon.
Can Moon Phases Vary in Duration?
Moon phases can vary slightly in duration due to factors such as the eccentricity of the Moon’s orbit, the tilt of its orbit, and atmospheric conditions. While there are average timeframes for each phase, variations can occur based on these factors.
What Cultural or Mythological Significance Do Moon Phases Have?
Moon phases hold significant cultural and mythological meanings across various societies throughout history. Here are some cultural and mythological significances associated with moon phases:
Lunar Calendars: Ancient civilizations, like the Mayans and Egyptians, developed lunar calendars based on the phases of the moon. These calendars were used for tracking time, determining agricultural cycles, and planning religious and cultural events.
Mythological Stories: Moon phases feature prominently in mythological stories and folklore. Different cultures have created legends and tales about the moon, attributing its changing phases to deities, celestial beings, or mythical creatures.
Symbolism and Rituals: Moon phases are symbolically linked to various aspects of life, such as fertility, growth, rebirth, and transformation. Many cultures incorporate moon phases into rituals, ceremonies, and spiritual practices, considering them auspicious times for specific activities or intentions.
Lunar Deities: Several mythologies include deities associated with the moon and its phases. These deities often embody qualities like femininity, wisdom, intuition, and the cycle of life. Examples include Artemis in Greek mythology and Chang’e in Chinese mythology.
Folklore and Superstitions: Moon phases have been linked to superstitions and beliefs in different cultures. For instance, the full moon has been associated with increased supernatural occurrences or changes in human behavior, giving rise to the idea of “lunacy” or “moon madness.”
The cultural and mythological significance of moon phases reflects the deep connection between humans and the celestial world. They have shaped beliefs, customs, and practices, adding a touch of mysticism and wonder to our understanding of the lunar cycle.
Conclusion
Moon phases are a fascinating and ever-present phenomenon that has captivated humans for centuries. From ancient civilizations to modern cultures, moon phases have held cultural, mythological, and symbolic significance. They have been used to track time, inspire stories and legends, guide rituals and ceremonies, and evoke a sense of wonder and mystery. The changing shapes of the moon, as it travels through its phases, have inspired awe and contemplation, leading to a deeper understanding of our place in the cosmos.
The moon phases have provided a source of inspiration for artists, poets, and scientists alike, fueling creativity and exploration. Whether we view the moon phases as scientific phenomena or embrace their cultural and mythological significance, they continue to hold a special place in our collective consciousness.
As we look up at the night sky and witness the waxing and waning of the moon, let us marvel at the beauty and complexity of the celestial dance. May the moon phases serve as a reminder of the vastness and wonder of the universe, inspiring us to explore, question, and appreciate the mysteries that lie beyond our earthly realm.

